Auto Scaling on Custom Metric
For this lab, you must have configured Prometheus and Grafana using help already. Refer to Lab K113 - HELM Package Manager - Kubernetes Tutorial with CKA/CKAD Prep to set it up.
Setup Nginx Ingress with Metrics
Delete existing nginx ingress controller setup with KIND
kubectl delete -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/main/deploy/static/provider/kind/deploy.yaml
Re deploy nginx ingress controller with helm, this time enabling the exposing the metrics which can then be scraped/collected by prometheus.
helm upgrade --install ingress-nginx ingress-nginx \
--repo https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx \
--namespace ingress-nginx --create-namespace \
--set controller.metrics.enabled=true \
--set controller.metrics.serviceMonitor.enabled=true --set \ controller.metrics.serviceMonitor.additionalLabels.release="prometheus" \
--set controller.hostPort.enabled=true \
--set controller.hostPort.ports.http=80 \
--set controller.hostPort.ports.https=443 \
--set-string controller.nodeSelector."kubernetes\.io/os"=linux \
--set-string controller.nodeSelector.ingress-ready="true"
Configure Prometheus to monitor Nginx Ingress
Update the existing Prometheus installation to support scrpaing services in all namespaces
assuming you deployed prometheus stack from kube-prometheus-stack path, switch to
cd ~/kube-prometheus-stack/
and upgrade
helm upgrade prom -n monitoring prometheus-community/kube-prometheus-stack --set grafana.service.type=NodePort --set grafana.service.nodePort=30200 --set prometheus.prometheusSpec.podMonitorSelectorNilUsesHelmValues=false --set prometheus.prometheusSpec.serviceMonitorSelectorNilUsesHelmValues=false
What this does is starts collecting metrics from services from all the namespaces not just the one in which prometheus is deployed. And it reads the annotations from the pods to figure out where to collect the metrics from.
Now, login to grafana and import custom dashboard for Nginx Ingress as
- Left menu (hover over +) -> Dashboard
- Click "Import"
- Enter the copy pasted json from https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/main/deploy/grafana/dashboards/nginx.json
- Click Import JSON
- Select the Prometheus data source
- Click "Import"
It may look similar to this, with possibly less data initially
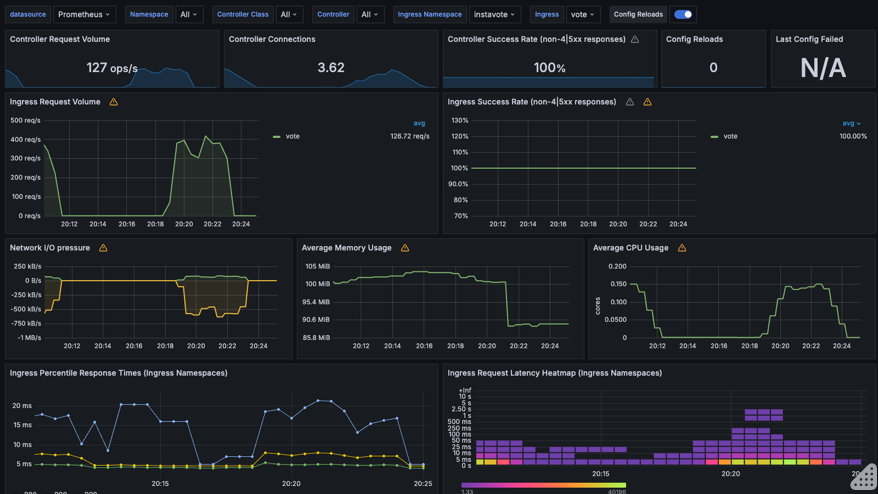
However, if you see some metric coming in, your setup with Nginx Ingress and Promethus Integration is working ! You may pat your back at this time :)
Setup Prometheus Adapter
Prometheus adapter converts the prometheus metrics and makes it available in kubernetes under custom.metrics.k8s.io api which can then read by the HPA and used as a input for autoscaling.
Begin by creating the configuration for this adapter to pick a specific metric from prometheus and expose it under custom API as,
File : prometheus-adapter-values.yaml
prometheus:
url: http://prom-kube-prometheus-stack-prometheus # Ensure this is correctly pointing to your Prometheus
port: 9090
rules:
default: false
custom:
- seriesQuery: 'nginx_ingress_controller_requests'
resources:
overrides:
namespace: {resource: "namespace"}
ingress: {resource: "ingress"}
name:
matches: "^nginx_ingress_controller_requests$"
as: "nginx_ingress_controller_requests_per_second"
metricsQuery: 'sum(rate(nginx_ingress_controller_requests{status=~"2.."}[2m])) by (namespace, ingress)'
- seriesQuery: 'nginx_ingress_controller_request_duration_seconds_bucket'
resources:
overrides:
namespace: {resource: "namespace"}
ingress: {resource: "ingress"}
name:
matches: "^nginx_ingress_controller_request_duration_seconds_bucket$"
as: "nginx_ingress_controller_latency"
metricsQuery: 'sum(rate(nginx_ingress_controller_request_duration_seconds_bucket{}[2m])) by (namespace, ingress, le)'
install the adapter as,
helm upgrade --install prometheus-adapter prometheus-community/prometheus-adapter -f prometheus-adapter-values.yaml -n monitoring
validate its running
kubectl get pods -n monitoring
validate that custom apis are working with
kubectl get --raw "/apis/custom.metrics.k8s.io" | jq .
kubectl get --raw "/apis/custom.metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1/namespaces/instavote/ingresses/vote/nginx_ingress_controller_requests_per_second" | jq .
kubectl get --raw "/apis/custom.metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1/namespaces/instavote/ingresses/vote/nginx_ingress_controller_latency" | jq .
with the second command, you are expected to see [sample output]
{
"kind": "MetricValueList",
"apiVersion": "custom.metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1",
"metadata": {},
"items": [
{
"describedObject": {
"kind": "Ingress",
"namespace": "instavote",
"name": "vote",
"apiVersion": "networking.k8s.io/v1"
},
"metricName": "nginx_ingress_controller_requests_per_second",
"timestamp": "2024-05-10T02:41:54Z",
"value": "0",
"selector": null
}
]
}
If you see this, your adapter configuration integratd with prometheus is set up and ready to be consumed by the hpa.
Configure Custom Autoscaling Policies
Add autoscaling policies based on the custom metric as
File : vote-custom-hpa.yaml
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: vote-custom
namespace: instavote
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: vote
minReplicas: 2
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- type: Object
object:
metric:
name: nginx_ingress_controller_requests_per_second
describedObject:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
name: vote
target:
type: Value
value: 100 # Target 200 requests per second per replica
- type: Object
object:
metric:
name: nginx_ingress_controller_latency
describedObject:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
name: vote
target:
type: Value
value: 50 # Target 50 milliseconds
behavior:
scaleDown:
policies:
- type: Pods
value: 2
periodSeconds: 120
- type: Percent
value: 25
periodSeconds: 120
stabilizationWindowSeconds: 60
selectPolicy: Min
scaleUp:
stabilizationWindowSeconds: 45
policies:
- type: Percent
value: 100
periodSeconds: 15
- type: Pods
value: 2
periodSeconds: 15
selectPolicy: Max
Apply it as
kubectl delete hpa vote
kubectl apply -f vote-custom-hpa.yaml
validate
kubectl get hpa
[sample output]
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
vote-custom Deployment/vote 0/100, 0/50 2 10 2 10h
now create a new load test config
File: loadtest-ing-job.yaml
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
generateName: loadtest-ing
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: siege
image: schoolofdevops/loadtest:v1
command: ["siege", "--concurrent=2", "--benchmark", "--time=4m", "http://vote.example.com"]
restartPolicy: Never
hostAliases:
- ip: "ww.xx.yy.zz"
hostnames:
- "vote.example.com"
backoffLimit: 4
where, replace ww.xx.yy.zz with the INTERNAL-IP address of the node which runs ingress which you can find using
kubectl get nodes -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
kube-control-plane Ready control-plane 47h v1.29.2 172.18.0.2 <none> Debian GNU/Linux 12 (bookworm) 6.8.0-31-generic containerd://1.7.13
kube-worker Ready <none> 47h v1.29.2 172.18.0.3 <none> Debian GNU/Linux 12 (bookworm) 6.8.0-31-generic containerd://1.7.13
kube-worker2 Ready <none> 47h v1.29.2 172.18.0.4 <none> Debian GNU/Linux 12 (bookworm) 6.8.0-31-generic containerd://1.7.13
in the above example, kube-worker is the node where ingress is running which has and ip address of 172.18.0.3. Thats what should be used in the load test config.
Before launching the load test, ensure that the http auth for the ingress is disabled. Remove the annotations block similar to follows from the ingress configuration for vote if you see it....
e.g. change the ingress spec from
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: vote
namespace: instavote
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-type: basic
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-secret: basic-auth
# message to display with an appropriate context why the authentication is required
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-realm: 'Authentication Required - Vote App'
to
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: vote
namespace: instavote
Finally create an instance of this job as,
kubectl create -f loadtest-ing-job.yaml
and now watch the scaling
watch 'kubectl top pods; kubectl get hpa; kubectl get pods'