Setup Promotion Pipeline with Kargo
Install Cert Manager
helm repo add jetstack https://charts.jetstack.io
helm repo update
helm install cert-manager jetstack/cert-manager --namespace cert-manager --create-namespace --set installCRDs=true
validate :
kubectl get all -n cert-manager
Install kargo
pass=$(openssl rand -base64 48 | tr -d "=+/" | head -c 32)
echo "Password: $pass"
hashed_pass=$(htpasswd -bnBC 10 "" $pass | tr -d ':\n')
signing_key=$(openssl rand -base64 48 | tr -d "=+/" | head -c 32)
Note: Remember to save the password which is echoed after echo "Password: $pass" step. You will need it later to login to kargo UI.
If you do not have htpasswd installed, install it as
On linux :
apt-get install apache2-utils
on macOS:
brew install httpd-tools
On windows:
choco install apache-utils
Once you generate the hashed_pass and signing_key, you could use them to install kargo using helm as,
helm upgrade --install kargo oci://ghcr.io/akuity/kargo-charts/kargo \
--namespace kargo \
--create-namespace \
--set api.adminAccount.passwordHash=$hashed_pass \
--set api.adminAccount.tokenSigningKey=$signing_key \
--set api.service.type=NodePort \
--set api.service.nodePort=30700 \
--wait
[sample output]
Release "kargo" has been upgraded. Happy Helming!
NAME: kargo
LAST DEPLOYED: Tue Feb 25 15:25:20 2025
NAMESPACE: kargo
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 2
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
.----------------------------------------------------------------------------------.
| _ _ _ _ _ |
| | | ____ _ _ __ __ _ ___ | |__ _ _ __ _| | ___ _(_) |_ _ _ |
| | |/ / _` | '__/ _` |/ _ \ | '_ \| | | | / _` | |/ / | | | | __| | | | |
| | < (_| | | | (_| | (_) | | |_) | |_| | | (_| | <| |_| | | |_| |_| | |
| |_|\_\__,_|_| \__, |\___/ |_.__/ \__, | \__,_|_|\_\\__,_|_|\__|\__, | |
| |___/ |___/ |___/ |
'----------------------------------------------------------------------------------'
Ready to get started?
⚙️ You've configured Kargo's API server with a Service of type NodePort.
The Kargo API server is reachable on port 30700 of any reachable node in
your Kubernetes cluster.
If a node in a local cluster were addressable as localhost, the Kargo API
server would be reachable at:
https://localhost:30700
🖥️ To access Kargo's web-based UI, navigate to the address above.
⚠️ Your API server is using a self-signed certificate and you should expect a
warning from your browser. You may safely disregard this.
⬇️ The latest version of the Kargo CLI can be downloaded from:
https://github.com/akuity/kargo/releases/latest
🛠️ To log in using the Kargo CLI:
kargo login https://localhost:30700 --admin --insecure-skip-tls-verify
📚 Kargo documentation can be found at:
https://docs.kargo.io
🙂 Happy promoting!
validate :
kubectl get all -n kargo
You should also be able to access the Kargo UI at https://NODEIP:30700
You would have to use the password you noted earlier to login.
Download and Install kargo CLI from Web UI opions
Example on linux,
wget -c https://github.com/akuity/kargo/releases/latest/download/kargo-linux-amd64
chmod +x kargo-linux-amd64
mv kargo-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/karg
validate
kargo
[sample output]
Usage:
kargo [flags]
kargo [command]
Available Commands:
apply Apply a resource from a file or from stdin
approve Manually approve a piece of freight for promotion to a stage
completion Generate the autocompletion script for the specified shell
config Manage Kargo CLI configuration
create Create a resource from a file or from stdin
dashboard Open the Kargo Dashboard in your default browser
delete Delete resources by file and names
get Display one or many resources
grant Grant a role to a user or grant permissions to a role
help Help about any command
login Log in to a Kargo API server
logout Log out of the Kargo API server
promote Promote a piece of freight
refresh Refresh a stage or warehouse
revoke Revoke a role from a user or revoke permissions from a role
server Start a local Kargo API server
update Update a resource
verify Verify a stage
version Show the client and server version information
Flags:
-h, --help help for kargo
Use "kargo [command] --help" for more information about a command.
Analyse the CRDs added by kargo
kubectl get crd
ubectl api-resources | grep -i kargo
# kubectl api-resources | grep -i kargo
clusterpromotiontasks clusterpromotask,clusterpromotasks kargo.akuity.io/v1alpha1 false ClusterPromotionTask
freights kargo.akuity.io/v1alpha1 true Freight
projects kargo.akuity.io/v1alpha1 false Project
promotions promo,promos kargo.akuity.io/v1alpha1 true Promotion
promotiontasks promotask,promotasks kargo.akuity.io/v1alpha1 true PromotionTask
stages kargo.akuity.io/v1alpha1 true Stage
warehouses kargo.akuity.io/v1alpha1 true Warehouse
Login to kargo using CLI
kargo login --admin --insecure-skip-tls-verify https://localhost:30700
Again, use the same password you noted earlier and used to login from the web UI.
Prepare to deploy the Guestbook App
Fork the guestbook app from https://github.com/sfd226/guestbook
Clone it to your local machine where you have docker setup
git clone https://github.com/XXXXXX/guestbook.git
where, replace XXXXXX with your github username.
Build a container image from the guestbook app
cd guestbook
docker image build -t ghcr.io/XXXXXX/guestbook:v1.0.3 .
where, replace XXXXXX with your github username. Ensure that you are using your personal github account so that you can control the access to the image repository etc.
Login to github container registry as per the instructions here
docker login ghcr.io
Push the container image to github container registry
docker push ghcr.io/XXXXXX/guestbook:v1.0.3
where, replace XXXXXX with your github username.
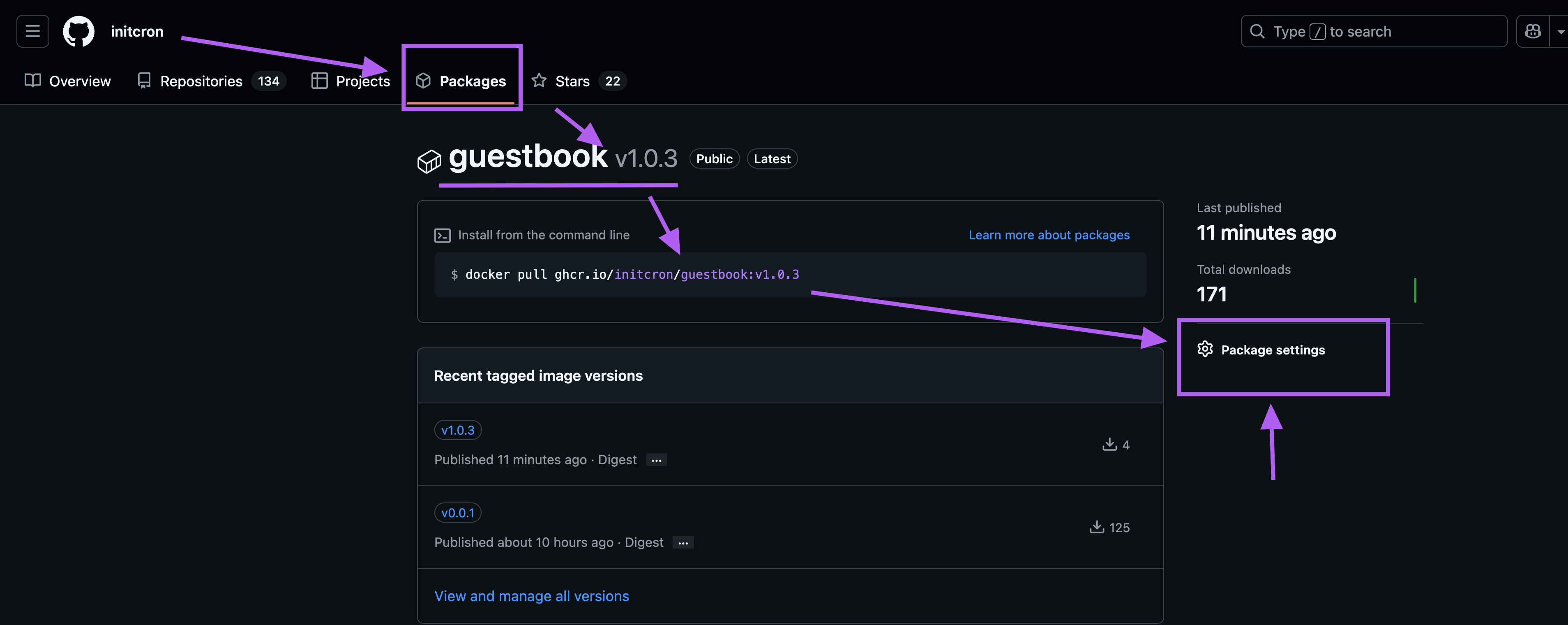
Validate that the image is available in github container registry by visting https://github.com/users/XXXXXX/packages
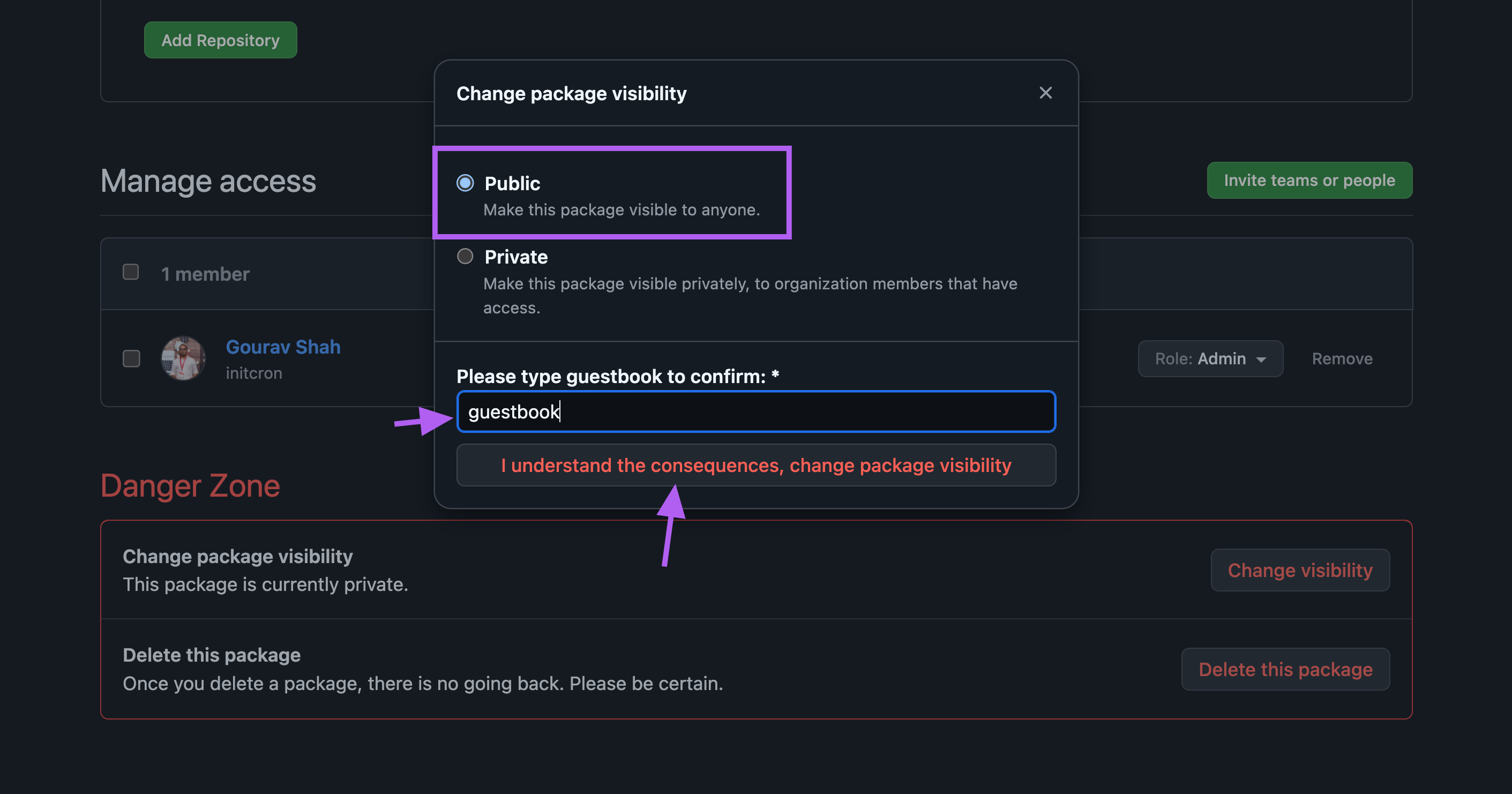
Make the package public by visting your package at https://github.com/users/xxxxxx/packages/container/package/guestbook and selecting "Package Settings".
From Danger Zone -> Change Vissibility , select "Public" and save.
Create Simple Promotion Workflow with Kargo
Fork the kargo-simple repo from https://github.com/sfd226/kargo-simple
Clone it to your local machine where you have kubernetes and argo setup already.
git clone https://github.com/XXXXXX/kargo-simple.git
where, replace XXXXXX with your github username.
Personalize the kargo-simple.yaml file with your github username and token.
cd kargo-simple
./personalize.sh <yourgithubusername>
Commit and push the personalized manifests to your forked repo.
git commit -a -m "personalize manifests"
git push origin main
Create a release branch from main branch from GiHub web UI.
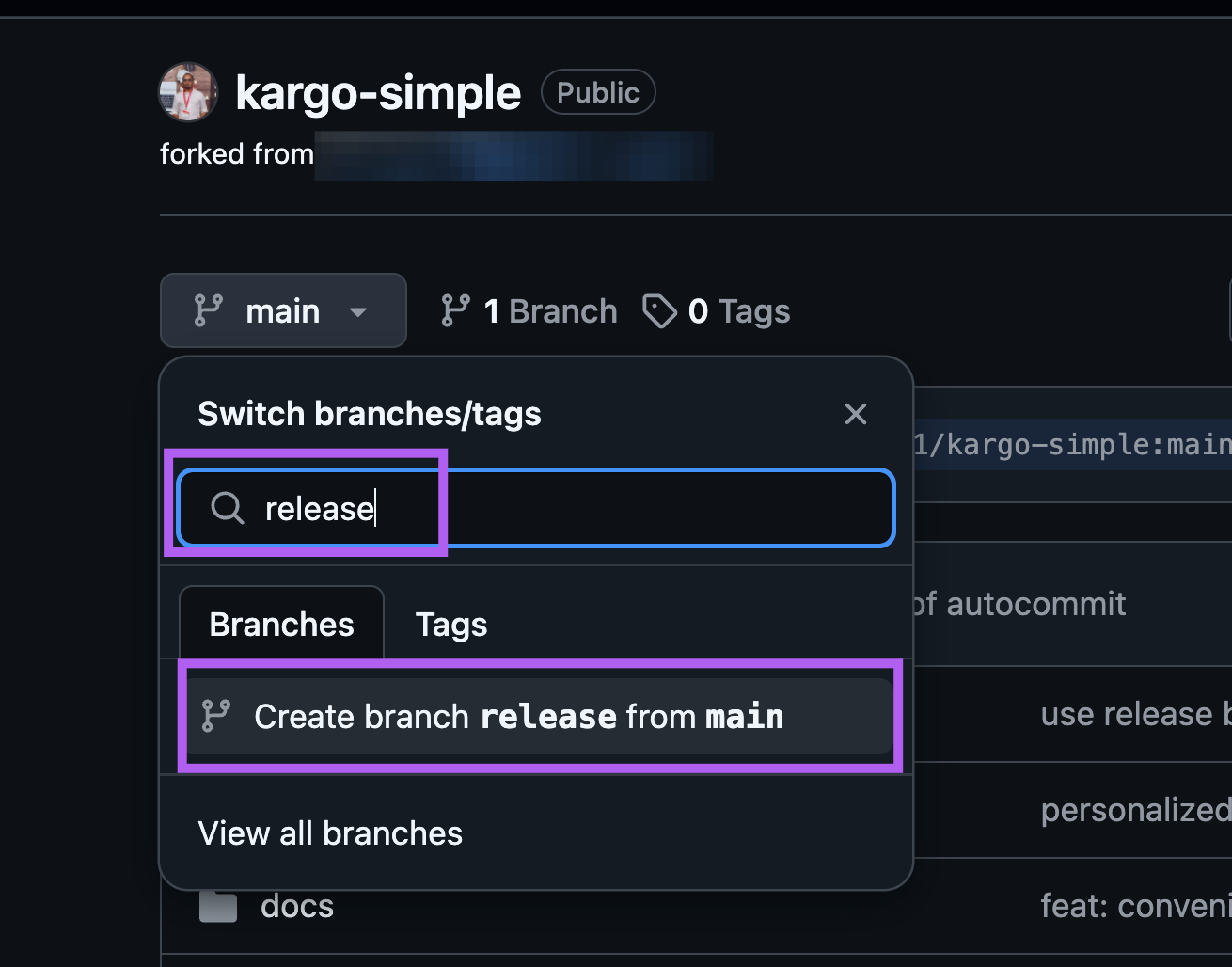
Create release branch is an important step, without which your deployments will not work. Make sure 'r' in release is smallcase
Deploy kargo app
cd kargo-simple
kargo apply -f ./kargo
[sample output]
project.kargo.akuity.io/kargo-simple created
promotiontask.kargo.akuity.io/promote created
promotiontask.kargo.akuity.io/promote-with-pr created
stage.kargo.akuity.io/dev created
stage.kargo.akuity.io/staging created
stage.kargo.akuity.io/prod created
warehouse.kargo.akuity.io/guestbook created
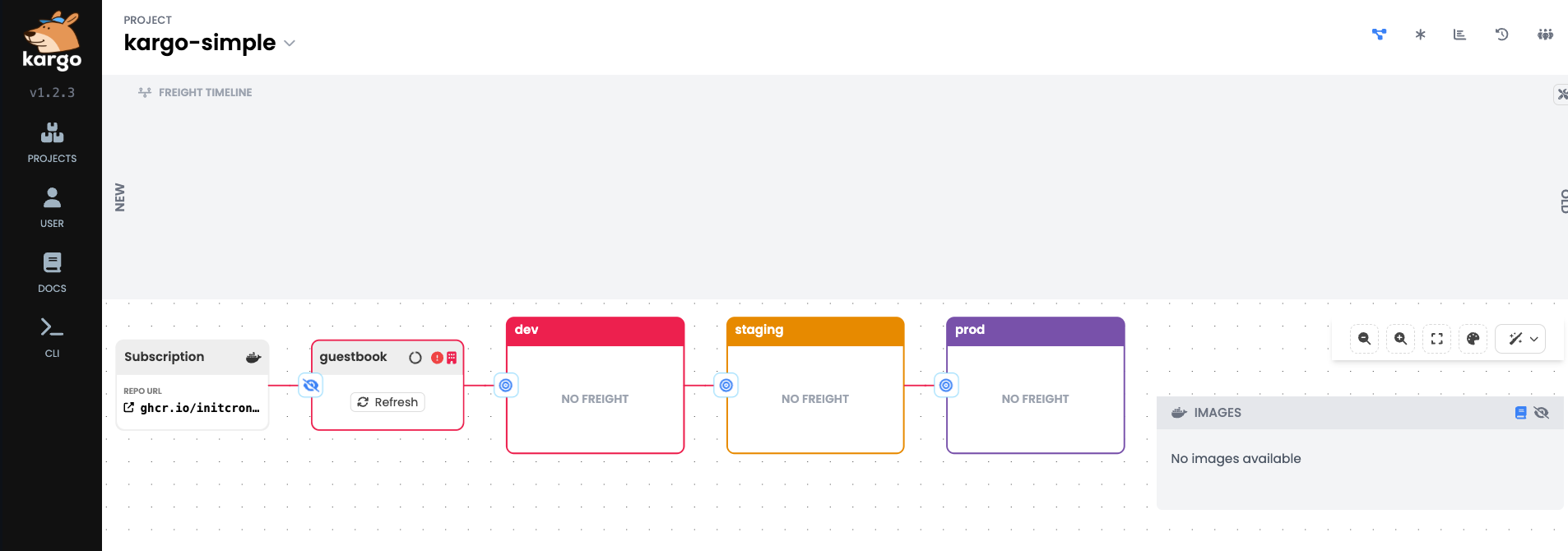
at this time, you shall see a kargo promotion workflow created for you with dev -> stage -> prod stages.
You could further examine the promotion workflow by clicking on the box which displays the name of the promotion workflow.
Add the Git repository credentials to Kargo.
kargo create credentials github-creds \
--project kargo-simple \
--git \
--username <yourgithubusername> \
--repo-url https://github.com/<yourgithubusername>/kargo-simple.git
--password <yourgithubtoken>
As part of the promotion process, Kargo requires privileges to commit changes to your Git repository, as well as the ability to create pull requests. Ensure that the given token has these privileges.
Create a ArgoCD app
Create Argo ApplicationSet to deploy guestbook app in three different environments viz dev, staging and prod using the command below,
kubectl apply -f argo/guestbook-appset.yaml
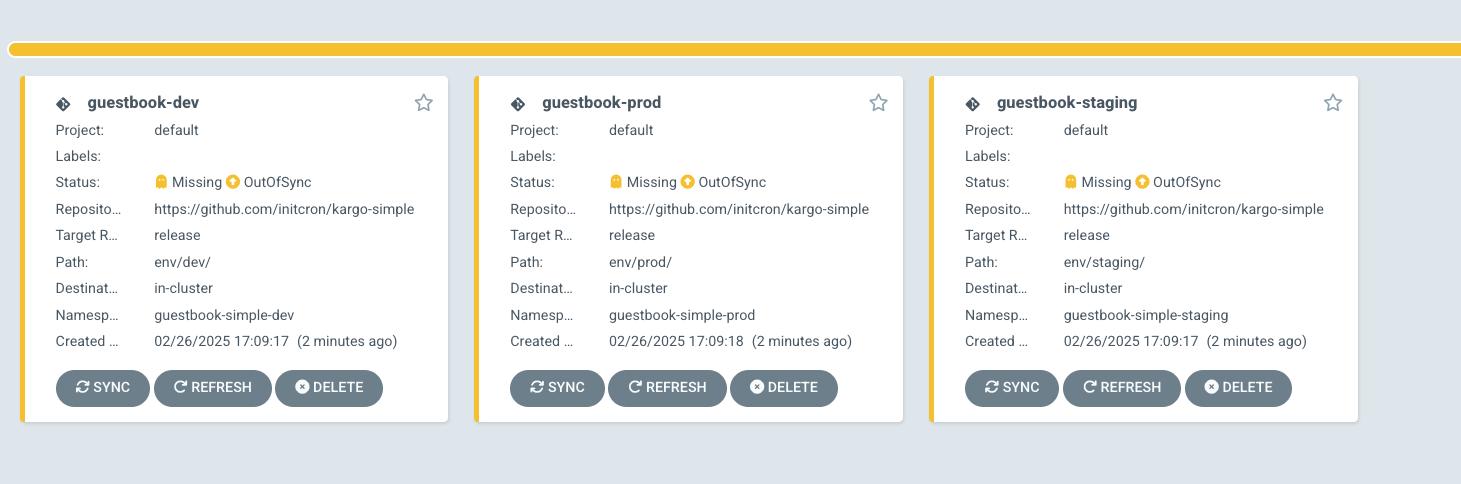
You shall see three applications created in Argo CD, with manual sync option, as we will trigger those using promotion workflows created with Kargo.
Simulate promotion of the guestbook app
Switch to guesstbook app repo abd make some change to public/index.html
For example, change the version number in the body tag to somet other number.
<title>Guestbook</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="header">
<h1>Guestbook 1.0.4</h1>
</div>
Build the container image and push it to github container registry.
docker image build -t ghcr.io/<yourgithubusername>/guestbook:v1.0.4 .
docker push ghcr.io/<yourgithubusername>/guestbook:v1.0.4
Now you should see a new freight available on kargo, which you could promote to dev by clickin on the target icon and selecting "Promote into stage" option.

Once promoted, you would also see the ArgoCD app is deployed to dev namespace from ArgoCD UI.
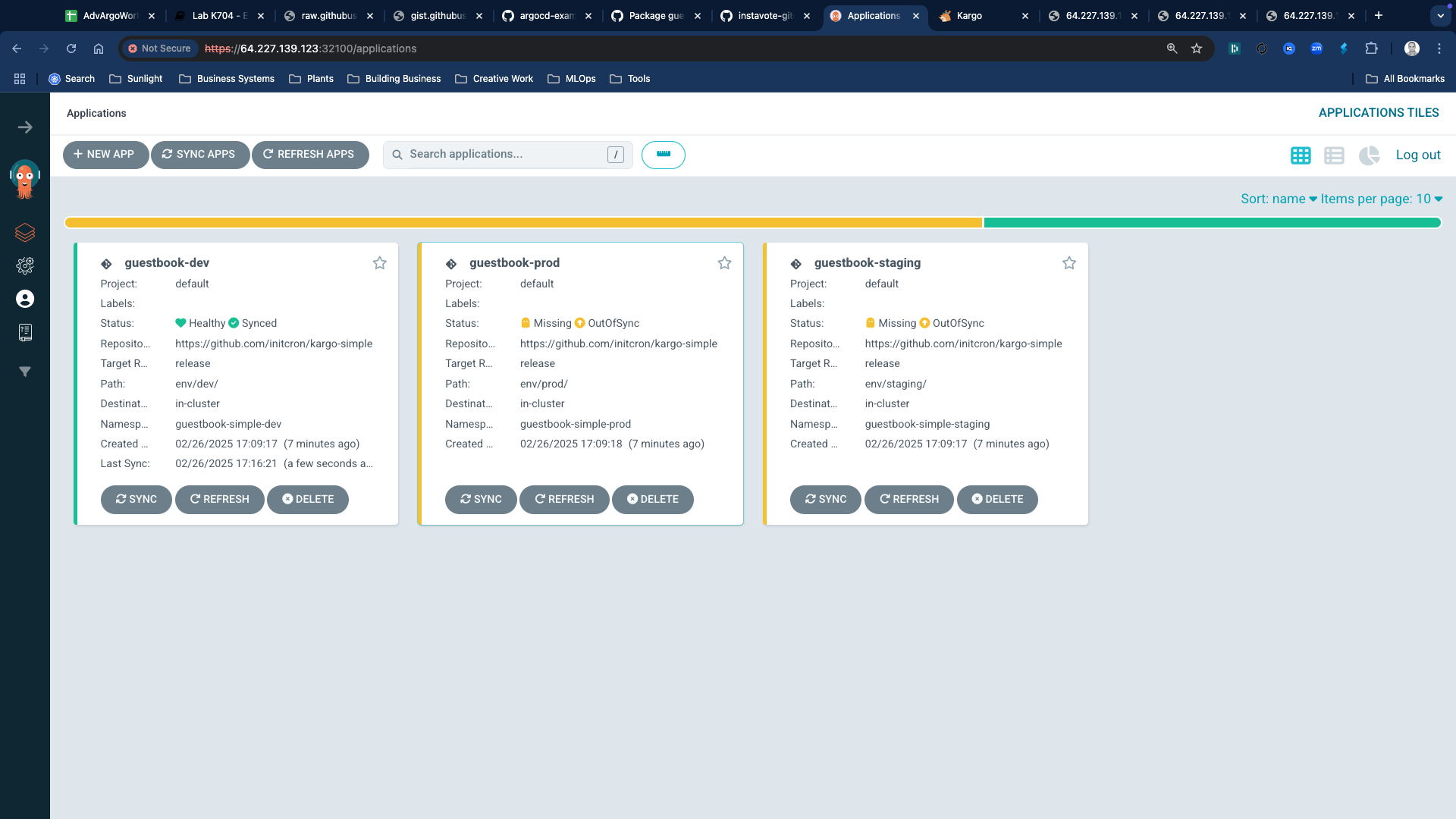
You could access the guestbook app at http://NODEIP:30100 for dev environment.
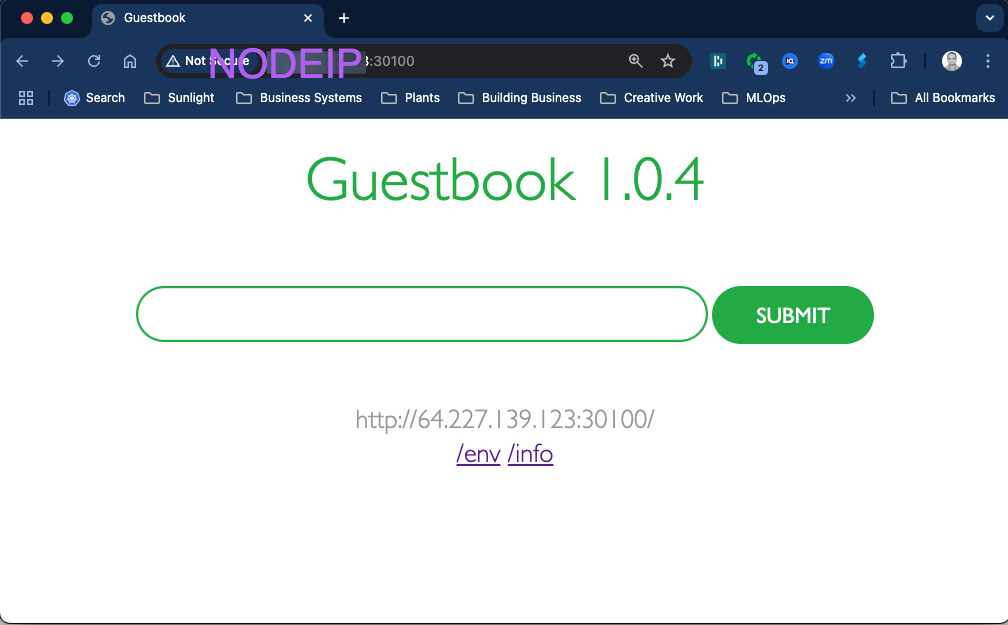
Yould could select the box which displays the name of the promotion workflow to see the promotions details
Setup Promotion Workflow
Here is an example of how Kargo promotes a new version of the guestbook app through the stages:
- Detect New Image:
docker image build -t ghcr.io/<yourgithubusername>/guestbook:v1.0.4 .
docker push ghcr.io/<yourgithubusername>/guestbook:v1.0.4
And you could keep on promoting it through the stages : Dev -> Stage -> Prod
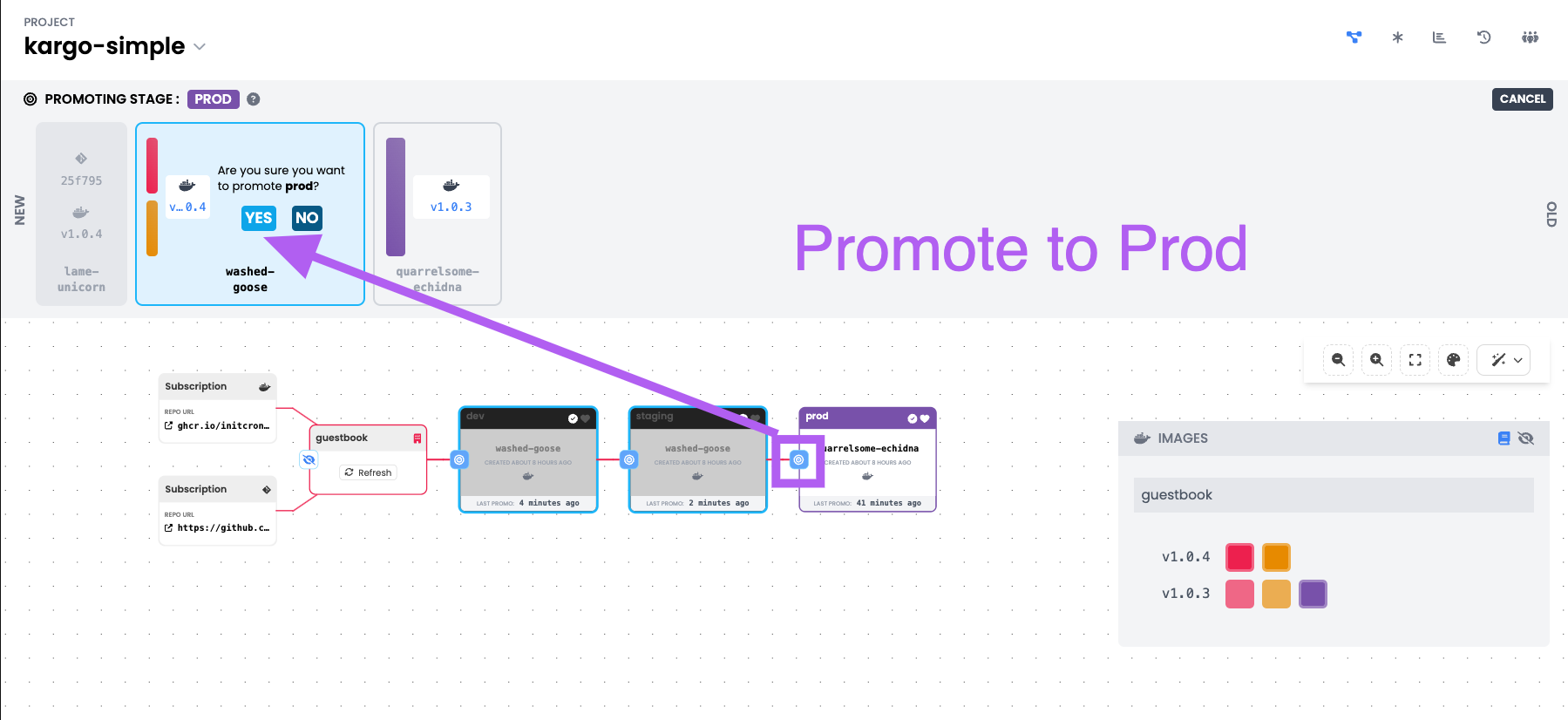
As you promote, you could access the guestbook app at
- http://NODEIP:30100 for dev environment
- http://NODEIP:30200 for staging environment
- http://NODEIP:30300 for prod environment
How Kargo Promotes Through Stages
Kargo automates the promotion of applications through different stages (e.g., dev, staging, prod) by detecting new container images and committing changes to the release branch based on the defined promotion workflow. Here's how it works:
1. Image Detection:
Kargo continuously monitors the container registry for new images. When a new image is pushed to the registry, Kargo detects it and creates a new "freight" representing the new version of the application.

2. Promotion Workflow:
The promotion workflow defines the stages through which the application must pass. Each stage can have specific criteria and manual approval steps. For example, the workflow might include stages like dev, staging, and prod.
3. Promotion to Dev:
When a new image is detected, Kargo promotes it to the dev stage. This involves updating the Kubernetes manifests with the new image tag and committing these changes to the release branch in the Git repository. Kargo then triggers the deployment of the updated manifests to the dev environment using ArgoCD.
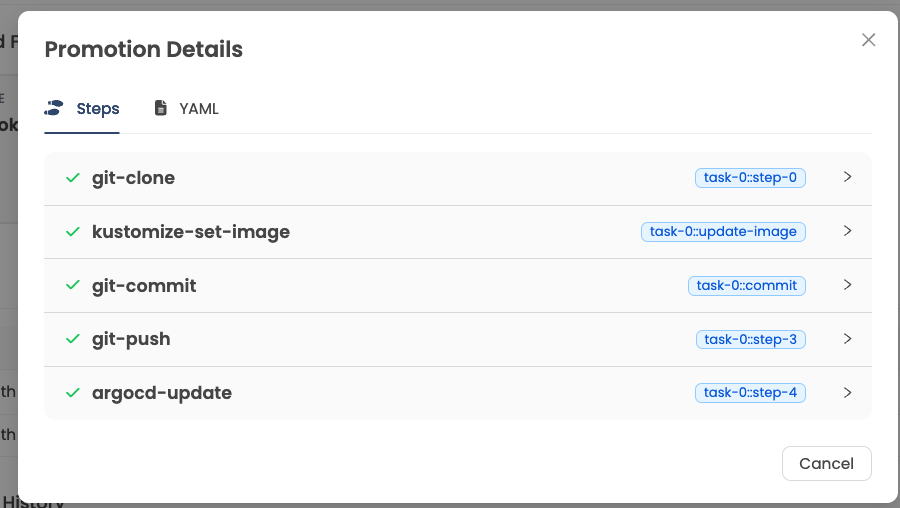
4. Manual Approval and Testing:
After the application is deployed to the dev environment, it undergoes testing and validation. If the tests pass and the application meets the criteria for promotion, a manual approval step may be required to promote the application to the next stage.
5. Promotion to Staging:
Once approved, Kargo promotes the application to the staging environment by repeating the process of updating the manifests, committing the changes, and triggering the deployment. The application undergoes further testing and validation in the staging environment.
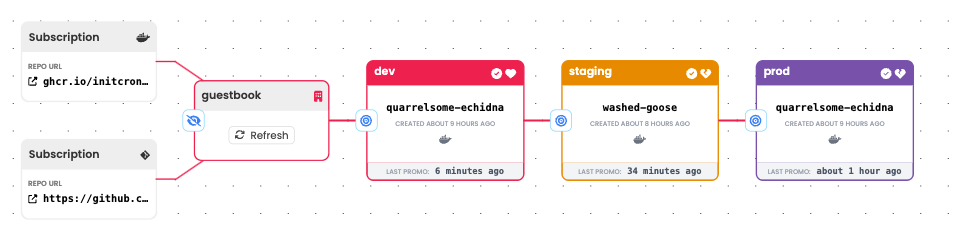
6. Promotion to Prod:
After successful validation in the staging environment, the application is promoted to the prod environment. This final promotion involves the same steps of updating manifests, committing changes, and triggering the deployment.
7. Commit Changes to Release Branch:
Throughout the promotion process, Kargo commits changes to the release branch in the Git repository. This ensures that the GitOps workflow is maintained, and the state of the application is always reflected in the Git repository.
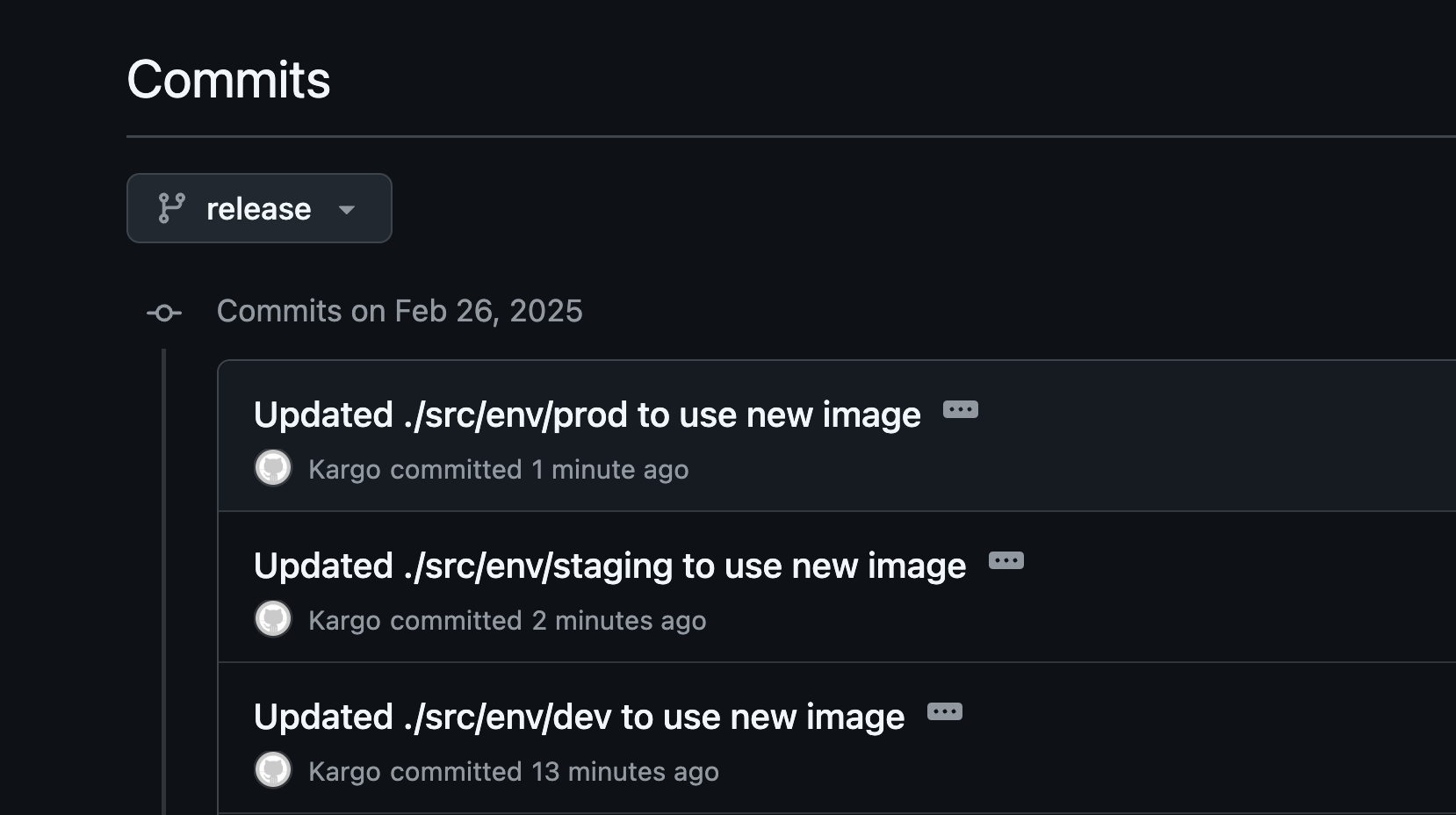
By automating the promotion process and integrating with ArgoCD, Kargo ensures that applications are deployed consistently and reliably across different environments. This approach minimizes the risk of manual errors and ensures that only validated and approved versions of the application are promoted to production.
Cleaning Up
Once you are done with the demo, you could delete the guestbook app deployments along with kargo configurations for it using the following commands.
kubectl delete -f argo/
kargo delete -f kargo/