Argo Events
Author: Gourav Shah
Publisher: School of Devops
Version : v2024.06.02.01
Project: Trigger CI Pipeline on GitHub Changes
Set up Argo Events
Launch Argo Workflow Environment with Killercoda , set up server UI and have it open.
Install Argo Events
kubectl create namespace argo-events
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-events/stable/manifests/install.yaml
# Install with a validating admission controller
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-events/stable/manifests/install-validating-webhook.yaml
kubectl apply -n argo-events -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-events/stable/examples/eventbus/native.yaml
Create RBAC Policies
kubectl apply -n argo-events -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-events/master/examples/rbac/sensor-rbac.yaml
kubectl apply -n argo-events -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-events/master/examples/rbac/workflow-rbac.yaml
Setup Components to Trigger CI Pipeline
You will now set up the components required for the Argo Events to trigger the CI workflow based on changes to GitHub. For this you are going to need
- Event Source - To listen to GitHub change events
- Sensor - Which activates on updated to event source and triggers the workflow
- Workflow Template - To create an instance of the CI Pipeline Workflow
- Container Registry Credentials - Used by the workflow to publish images with
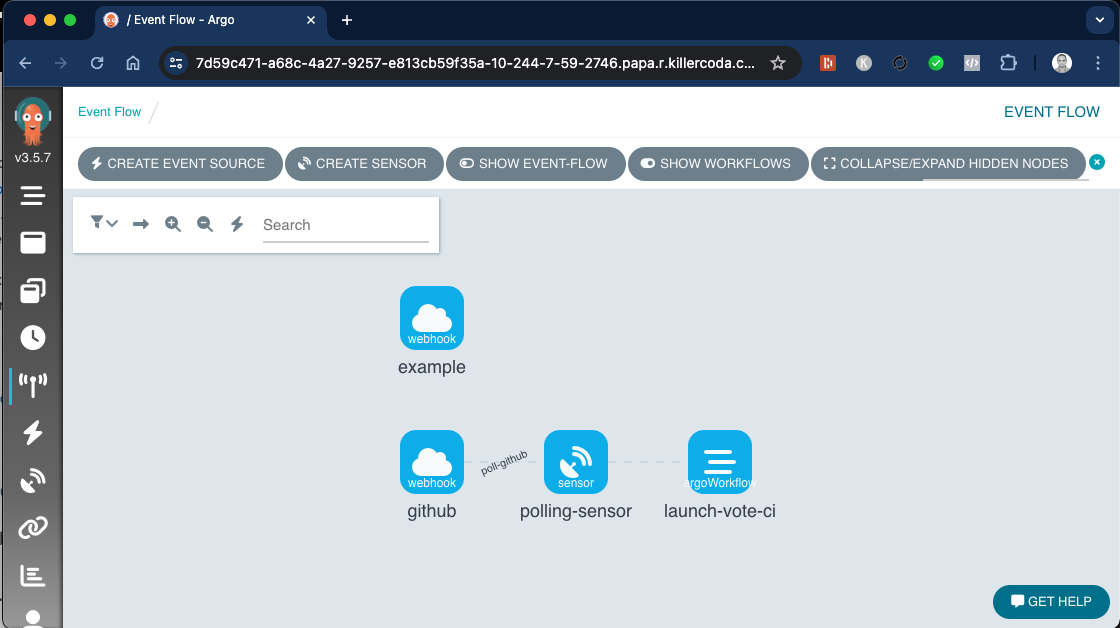
Create an Argo Events EventSource and Sensor to handle the events sent by your polling job.
File: webook-eventsource.yaml
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: EventSource
metadata:
name: webhook
namespace: argo-events
spec:
service:
ports:
- port: 12000
targetPort: 12000
webhook:
example:
port: "12000"
endpoint: /example
method: POST
github:
port: "12000"
endpoint: /github
method: POST
apply
kubectl apply -f webook-eventsource.yaml
Check the Argo Workflow for Vote CI Pipeline converted into a Workflow Template.
Create workflow template using this code as
kubectl apply -f https://gist.githubusercontent.com/gouravjshah/c1704b560909f424e66062d86af9ff5c/raw/f7c5f73605a732d358a93854bc2da652113de494/vote-ci-template.yaml
validate
kubectl get workflowtemplate -A
argo template list -A
add registry credentials to argo-events namespace again with
kubectl create secret -n argo-events docker-registry docker-registry-creds \
--docker-server=https://index.docker.io/v1/ \
--docker-username=xxxx --docker-password=yyyy
where replace,
xxxxwith registry usernameyyyywith registry access token
Add sensor which will listen to updates to github webhook created with event source and then trigger the argo workflow as,
File : sensor.yaml
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Sensor
metadata:
name: polling-sensor
namespace: argo-events
spec:
template:
serviceAccountName: operate-workflow-sa
dependencies:
- name: poll-github
eventSourceName: webhook
eventName: github
triggers:
- template:
name: launch-vote-ci
argoWorkflow:
operation: submit
source:
resource:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: ci-pipeline-
spec:
workflowTemplateRef:
name: vote-ci-template
arguments:
parameters:
- name: repo-url
value: "https://github.com/xxxxxx/vote.git"
- name: branch
value: "main"
- name: image
value: "xxxxxx/vote"
- name: dockerfile
value: "Dockerfile"
where,
- replace
repo-urlwith your code repository url - update image tag by replacing
xxxxxxwith your docker hub user name
apply
kubectl apply -f sensor.yaml
validate
kubectl get pods -n argo-events
you could also check the logs for sensor controller (useful for troubleshooting) using
kubectl logs -n argo-events -l "controller=sensor-controller"
you should see a new pod launched to run this sensor.
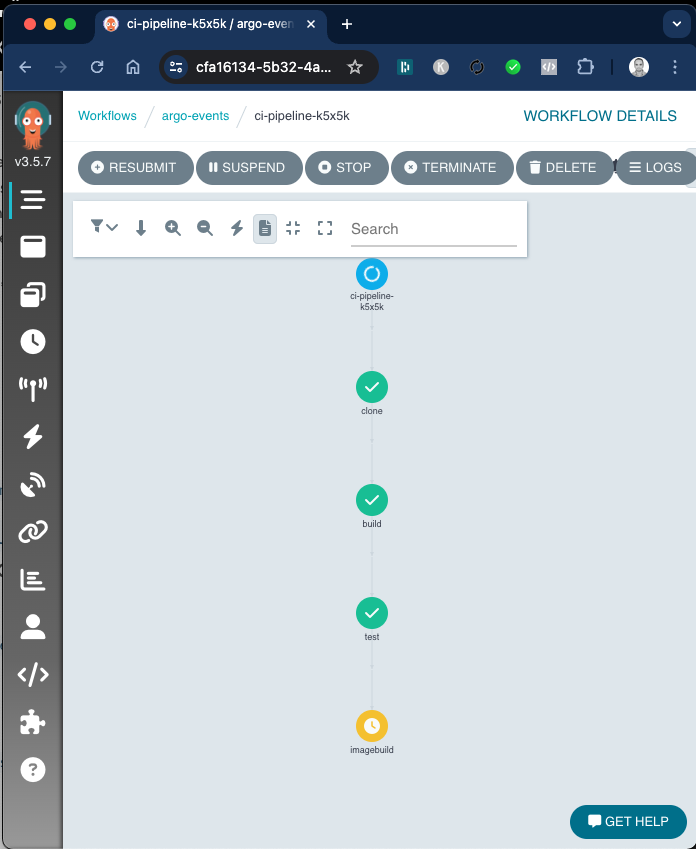
At this time, if you have Argo Workflow set up, you should see a event flow such as this
Event Flow :
Deploy GitHub Poller
After setting up the event flow, you also need to set up something which will trigger the event source on changes to GitHub.
You could do this in two ways
- Using Webhooks : You could expose the event source service to outside and let GitHub trigger a webhook whenever there is a push event. This is useful if your event source can be publically available (GitHub can connect to it).
- In-cluster Polling : You could alternately set up in cluster system to periodically poll GitHub for changes, and trigger the event source. This is useful when you can not expose event source service pubically, and are running your cluster in a private network.
Since we do not assume your cluster is public, we will employ the second approach.
To achisve in-cluster polling, create the following Kubernetes CronJob that periodically polls GitHub for new commits. If new commits are found, the job can trigger the event source webhook created earlier.
File: poller-cronjob.yaml
---
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: CronJob
metadata:
name: github-polling-job
spec:
schedule: "* * * * *" # Poll every minute
jobTemplate:
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: poller
image: schoolofdevops/github-poller:latest
env:
- name: GITHUB_API_URL
value: "https://api.github.com/repos/yourusername/yourrepo/commits"
- name: GITHUB_TOKEN
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: github-token-secret
key: token
- name: LAST_COMMIT_FILE
value: "/data/last_commit.txt"
- name: ARGO_EVENT_SOURCE_URL
value: "http://webhook-eventsource-svc.argo-events.svc.cluster.local:12000/github"
volumeMounts:
- name: commit-storage
mountPath: /data
restartPolicy: OnFailure
volumes:
- name: commit-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: poller-pvc # Use a PVC to persist the last commit file
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: poller-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Mi
where,
- replace value of
GITHUB_API_URLto match your user name and repo components e.g.https://api.github.com/repos/devops-0001/vote/commits - verify values for all env variables to be correct
Also create secret with github token with access to the repository, which is used in the cronjob above.
kubectl create secret generic github-token-secret --from-literal=token=xxxx
replace xxxx with actul GitHub access token.
create this cronjob as
kubectl apply -f poller-cronjob.yaml
now start watching the cronjobs as well as event flow from Argo Workflow dashboard.
Event Flow :
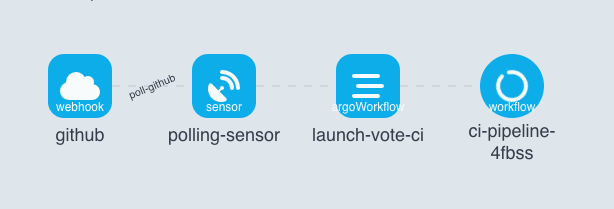
Workflows: