Application Routing with Ingress Controllers
Pre Requisites
- Ingress controller such as Nginx, Trafeik needs to be deployed before creating ingress resources.
- On GCE, ingress controller runs on the master. On all other installations, it needs to be deployed, either as a deployment, or a daemonset. In addition, a service needs to be created for ingress.
- Daemonset will run ingress on each node. Deployment will just create a highly available setup, which can then be exposed on specific nodes using ExternalIPs configuration in the service.
Getting Ready to add Traffic Management - Set up Nginx Ingress Controller
An ingress controller needs to be created in order to serve the ingress requests. As part of this lab you are going to use Nginx as the ingress controller. Its a fast and lightweight ingress controller and also comes with great documentation and support.
+----+----+--+
| ingress |
| controller |
+----+-------+
You are going to setup ingress controller using helm. Assuming helm is already installed, begin adding the repository to install nginx as a ingress controller from:
Install helm to setup Nginx Ingress Controller. To install helm version 3 on Linux or MacOS, you can follow following instructions.
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/master/scripts/get-helm-3 | bash
You could further refer to Official HELM Install Instructions for alternative options.
Verify the installtion is successful,
helm --help
helm version
Launch Nginx Ingress controller using helm as :
helm upgrade --install ingress-nginx ingress-nginx \
--repo https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx \
--namespace ingress-nginx --create-namespace \
--set controller.hostPort.enabled=true \
--set controller.service.type=NodePort \
--set controller.hostPort.ports.http=80 \
--set-string controller.nodeSelector."kubernetes\.io/os"=linux \
--set-string controller.nodeSelector.ingress-ready="true"
Check the pod for Nginx Ingress, if its running
kubectl get pods -n ingress-nginx
You may see the pod in pending state. Check why its pending by describing it.
Once you describe, you will see that its pending because it has a nodeSelector defined which is looking for a node with label set to ingress-ready="true".
Check the label on the current nodes
kubectl get nodes --show-labels
Add this lable to first of the worker nodes as
kubectl label node kind-worker ingress-ready="true"
validate
kubectl get nodes --show-labels
This time you should see the label added, and nginx ingress controller running, which can be validated using
kubectl get pods -n ingress-nginx --watch
Wait for the container for nginx ingress controller to be up. You could also validate by connecting to the IPADDRESS of your node where the cluster is being setup on port 80, where you should see **404 Not Found** error. This is the sign that nginx is set up as a ingress controller and looking for a request with hostname/path defined.
Add Ingress Rule with Host based Routing
We will direct all our request to the ingress controller now, but with differnt hostname e.g. vote.example.com or results.example.com. And it should direct to the correct service based on the host name.
In order to achieve this you, as a user would create a ingress object with a set of rules,
+----+----+--+
| ingress |
| controller |
+----+-------+
| +-----+----+
+---watch----> | ingress | <------- user
+----------+
File : vote-ing.yaml
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: vote
namespace: instavote
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
rules:
- host: vote.example.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: vote
port:
number: 80
And apply
kubectl get ing
kubectl apply -f vote-ing.yaml --dry-run
kubectl apply -f vote-ing.yaml
Since the ingress controller is constantly monitoring for the ingress objects, the moment it detects, it connects with nginx and creates a rule as follows.
+----------+
+--create----> | nginx |
| | rules |
| +----------+
+----+----+--+ ^
| ingress | :
| controller | :
+----+-------+ :
| +-----+----+
+---watch----> | ingress | <------- user
+----------+
where,
- A user creates a ingress object with the rules. This could be a named based or a path based routing.
- An ingress controller, in this example nginx constantly monitors for ingress objects. The moment it detects one, it creates a rule and adds it to the nginx load balancer. This rule maps to the ingress specs.
Where,
-
vote.example.com is added as frontend. This frontends point to service vote.
-
respective backend also appear on the right hand side of the screen, mapping to each of the service.
Add Local DNS
You have created the ingress rules based on hostnames e.g. vote.example.com and results.example.com. In order for you to be able to access those, there has to be a dns entry pointing to your nodes, which are running nginx.
vote.example.com -------+ +----- vote:81
| +-------------+ |
| | ingress | |
+===> | node:80 | ===+
| +-------------+ |
| |
result.example.com -------+ +----- result:82
To achieve this you need to either,
- Create a DNS entry, provided you own the domain and have access to the dns management console.
- Create a local hosts file entry. On unix systems its in
/etc/hostsfile. On windows its atC:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts. You need admin access to edit this file.
For example, on a linux or osx, you could edit it as,
sudo vim /etc/hosts
And add an entry such as ,
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx vote.example.com result.example.com kube-ops-view.example.org
where,
- xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is the actual IP address of one of the nodes running nginx.
And then access the app url using http://vote.example.com
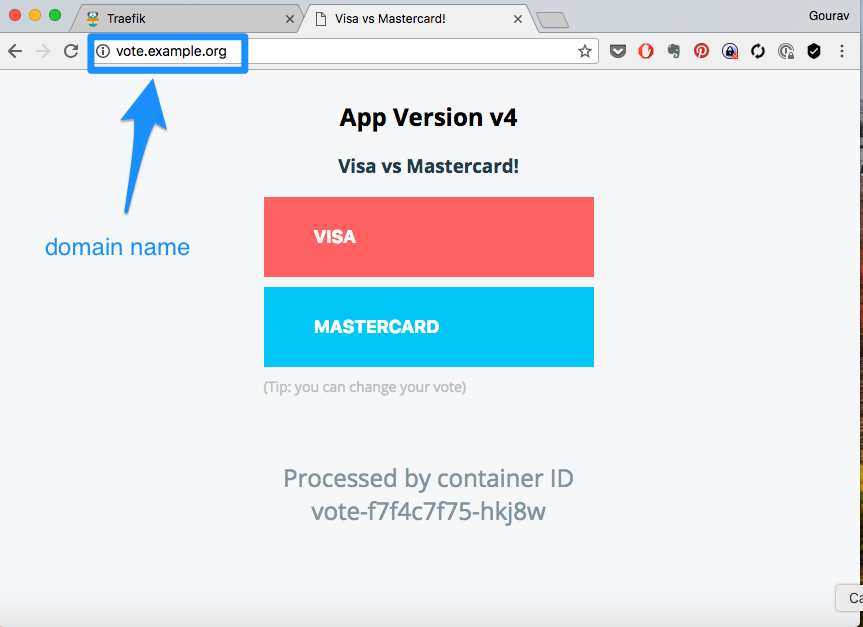
Add another Web Application with Ingress
kubectl create deployment nginx --image=nginx
kubectl create service clusterip nginx --tcp=80
Add ingress rule
file: result-ing.yaml
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: web
namespace: instavote
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
rules:
- host: web.example.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: nginx
port:
number: 80
And update hosts file with new route as ,
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx vote.example.com web.example.com kube-ops-view.example.org
Visit http://web.example.com:30400 to see your request being routed to nginx web page.
Mini Project : Configure Ingress for Result App
Now that you have added the ingress rule for the vote app, follow the same method and add one for the result app as well which is running in the same namespace.
The final validation would be, when you access or http://result.example.com you should see it pointing to the result app.
References
Keywords
- nginx on kubernetes
- kubernetes ingress
- kubernetes annotations
- daemonsets